Computer Network Basic
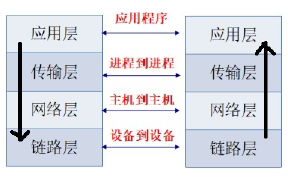
Network hierarchy
Seven-layer model
Application layer: protocol APP for application layer Representation layer: converting computer-recognized binary into human-recognized data Session layer: analyze the communication status of the data Transport layer: process and inter-process communication (port information) Network layer: host-to-host pass (IP address) Data link layer: complete frame data sent and received (transmitted independently on the network) mac address (device address) Physical layer: not the physical device, but the type of interface on the physical device, the strength of the current
4 Layers Protocol: TCP/IP protocol layer
Application layer: protocols for the application layer is FTP、Telnet、HTTP Transport layer (transport layer): process and inter-process communication (port information) TCP, UDP Network layer: host-to-host pass (IP address) IP, ICMP Link layer: complete frame data sent and received (transmitted independently on the network) mac address (device address) ARP RARP
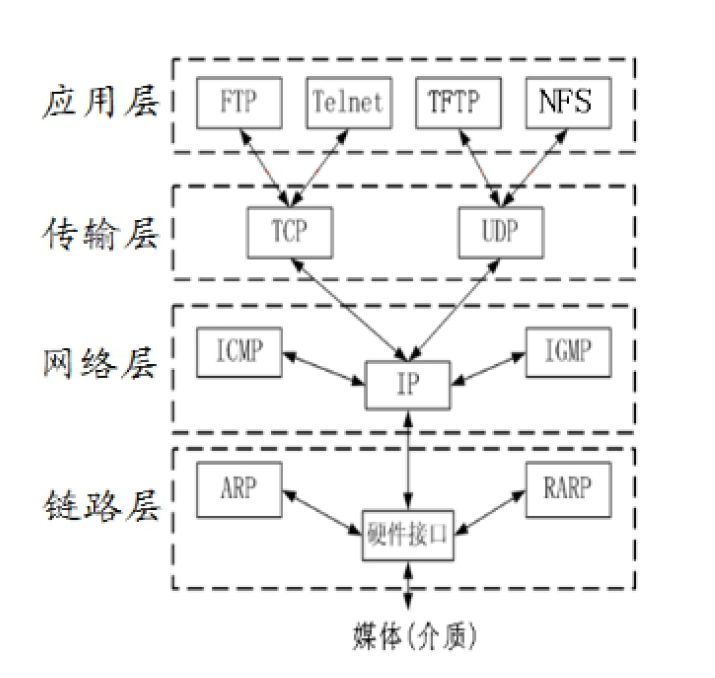
- IP Protocol Inter-networking Protocol (Network Layer)
The transmission of packets(Internet packets) from source address to destination on an interconnected network system provides the necessary functionality capable protocol Try to send data from the source address to the destination Features. Unreliable: it does not guarantee that an IP packet will successfully reach its destination and provides only best-effort transmission Connectionless: IP does not maintain any information about the status of subsequent packets. Each packet is processed independently of each other. IP packets can be received out of order of delivery IP packets contain the IP address of the host sending it (source address) and the IP address of the host receiving it (destination address)
- TCP is a connection-oriented, reliable transport layer communication protocol.
Functions. Provides communication between processes on different hosts Features.
- establish link->use link->release link (virtual circuit)
- TCP packets contain serial numbers and acknowledgement serial numbers
- packets are sorted and error checked, while corrupted packets can be retransmitted
Service object UDP protocol User Datagram Protocol (transport layer)
Services that require high reliability and are connection-oriented such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc. Summary: TCP Link Oriented Reliable Sorting Error checking Failure retransmission No broadcast support
- UDP Protocol User Datagram Protocol (Transport Layer)
UDP is a connectionless oriented transport layer communication protocol
Functionality. Provides inter-process communication on different hosts Features
- no link needs to be established before sending data
- no checking of packet order
- no error detection and retransmission mechanism
Service Object Mainly used for "query-answer" services Such as: NFS, NTP, DNS, etc. Summary: UDP no connection no sequencing, no error checking, no retransmission, fast, broadcast support
Address Introduction
- mac address (link layer) Device and device communication
MAC address, used to identify network devices, similar to an ID number, and theoretically unique worldwide. Composition: MAC address within Ethernet is a 48bit value

- IP address IPv4 (network layer) host and host 32bit
IP address composition: use 32bit, composed of two parts {network ID, host ID} Subnet ID: the consecutive bits of the IP address covered by 1 in the subnet mask Host ID: the consecutive bits of the IP address covered by 0 in the subnet mask
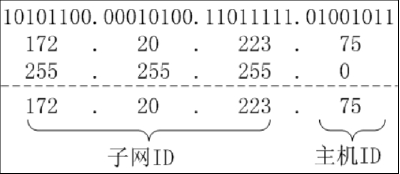
IP and subnet mask used together.
192.168.0.111/255.255.255.0 == 192.168.0.111/24 192.168.0.111/255.255.0.0 == 192.168.0.111/16 192.168.0.111/255.0.0.0 == 192.168.0.111/8
ip address characteristics:different network segments can not communicate directly
Networks with different subnet IDs cannot communicate directly, if they want to communicate, they need to be forwarded by the router IP addresses with all 0 host IDs represent network segment addresses. The IP address with host ID of 1 indicates the broadcast address of the network segment.
Example: 192.168.0.111/255.255.255.0 Ask the current IP address of the segment 192.168.0.0 and the broadcast address 192.168.0.0. address 192.168.0.255
Note: Neither the segment address nor the broadcast address in any of the segments can be assigned to a host 192.168.0.1~192.168.0.254 == the number of available IPs is only 254 Case: 192.168.0.111/255.255.0.0 Ask the segment address 192.168.0.0 and the broadcast address 192.168.255.0.0 of the current IP address192.168.255.255 available hosts 1~65534 == number of available IPs only 65534
- IP address classification (more reasonable use of IP addresses)
Class A address: default 8bit subnet ID, the first one is 0 WAN (country - country, big city - big city) 0xxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx/255.0.0.0 Class B address: default 16bit subnet ID,the first two digits are 10 MAN (city-city) 10xx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx/255.255.0.0 Class C address: default 24bit subnet ID,the first three digits are 110 110x xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx/255.255.255.0 LAN Class D address: the first four bits are 1110, multicast address Class E address: the first five bits are 11110, reserved for future use
Class A,B,C addresses are the most commonly used
Public IP (can be directly connected to the Internet) IP unified by InterNIC Private IP (not directly connected to the Internet) Mainly used for host connection planning in local area network

Loopback address
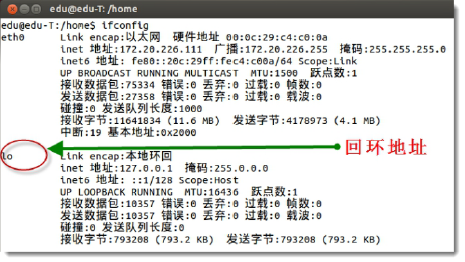
Function The main purpose is to test the network configuration of this machine, being able to ping through 127.0.0.1 means This means that there is no problem with the installation of NIC and IP protocol on this machine. Note Any address in 127.0.0.1~127.255.255.254 will be looped back to the local host does not belong to any of the classed address categories, it represents the local virtual interface of the device Set the Linux IP sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.222 netmask 255.255.255.0
subnet mask (also called network mask, address mask) is a 32-bit value consisting of 1 and 0, and 1 and 0 are consecutive. Features:
- Must be used in conjunction with IP address, cannot exist alone
- The consecutive bits in the IP address covered by 1 in the subnet mask are the subnet ID, and the rest are the host ID.
port number: similar to a pid to identify a process; in a network program, the port number is used to identify a running network program
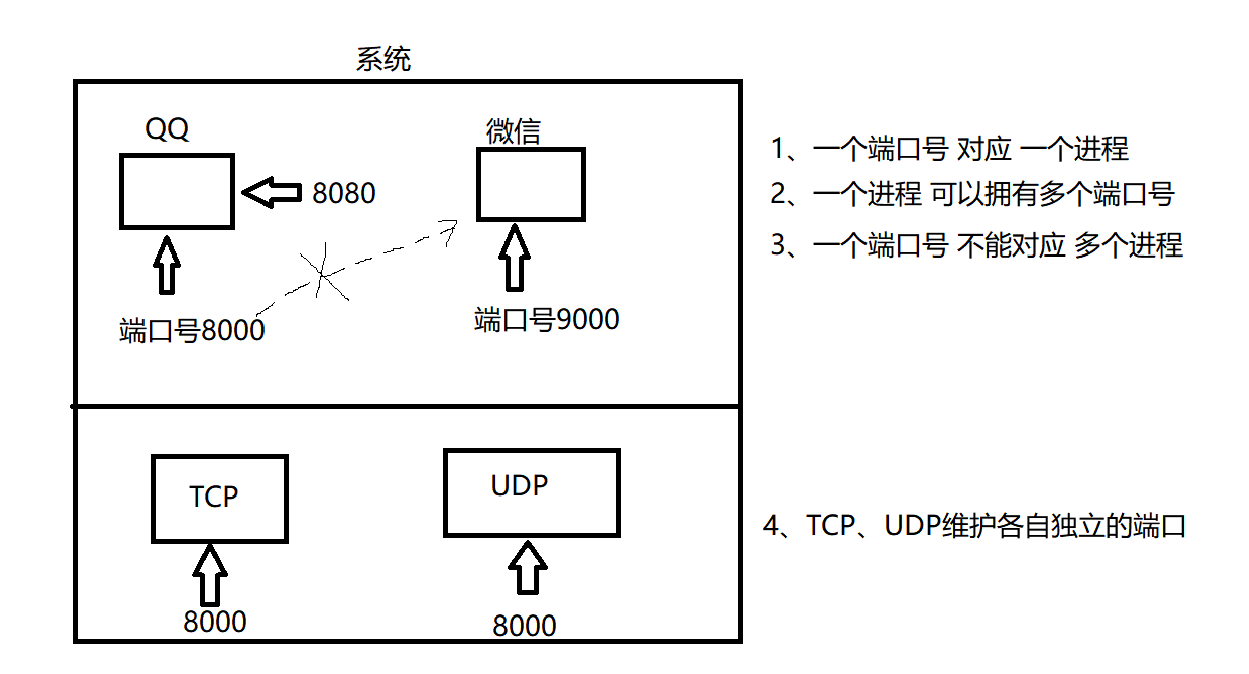 Features
Features
- The port number is an unsigned short integer type
- Each port has a port number
- TCP, UDP maintain their own independent port number
- Network applications must occupy at least one port number, but can also occupy multiple port numbers
- Classification of ports
Well-known ports (1~1023) Uniformly assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) according to user needs For example: FTP-21, HTTP-80, etc. The range normally used by servers; if forced to use, root privilege must be added Dynamic port (1024~65535) The range normally used by applications Note Port number is similar to process number, only one process can be marked at the same time Can be used repeatedly